From Colombia to Ghana to Canada, communicating with members of parliament, tracking city council spending, and advocating for environmental oversight of extractive industries are among a wide range of governance activities that have become possible for anyone with access to an internet connection, a computer, or a smartphone. That’s a lot of people, but not nearly enough.
FrontlineSMS at 7: Nigerian Mobile Election Monitors, 2007, from our Founder, Ken Banks
In the second of our seven blog posts celebrating the month that FrontlineSMS turns seven, our Founder Ken Banks reflects on one of the first users of our free, award-winning platform and the example that put us in the headlines for the first time. See a slideshow of our users showing off their work here.
"I'm often asked what my favourite FrontlineSMS deployment is."I don't really have a personal favourite - they're all interesting and inspiring in their own way. But if you asked me what I thought was organisationally one of the most important FrontlineSMS deployments, I'd have to say its use in the 2007 Nigerian Presidential Elections.
"I was at Stanford University on a Fellowship at that time and, although FrontlineSMS was ticking over quite nicely it wasn't having the kind of impact I was hoping for. I was even considering shutting it down - what a mistake that would have been.
"Suddenly, one weekend in April 2007, the mainstream media got hold of a story that an ad-hoc coalition of Nigerian NGOs, under the banner of NMEM (Nigerian Mobile Election Monitors), had monitored their elections using FrontlineSMS. As Clay Shirky has pointed out since, this was groundbreaking, and it was being done by grassroots NGOs on their own terms. This is exactly what FrontlineSMS was designed to do. As media interest picked up, downloads went up and donors began paying increasing amounts of attention. That summer the MacArthur Foundation stepped in with the first FrontlineSMS grant - $200,000 for a software rewrite.
"Without NMEM this would never have happened, and we wouldn't be where we are today. For that reason I'd have to choose it as one of my all-time favourite deployments. Thanks again, guys. What you did has indirectly helped thousands more dedicated, grassroots NGOs like yours, all over the world".
Starting today, we’re collecting photos of our users telling the world how they use FrontlineSMS. If you want to get in on the act, take a photo of yourself or your team holding a piece of paper or a whiteboard telling the world what you do with FrontlineSMS. For example: ‘I monitor elections’, ‘I safeguard children’ or ‘I make art’. You can see a slideshow of the photos we’ve had so far on our Flickr page.
It doesn’t matter what language it’s in as long as it’s legible and if possible you should be able to see from the photo where it was taken, so, if you can, get out of the office!
You can: - post to Twitter or Instagram with the hashtag #FrontlineSMSat7 - email the picture and we’ll post them - post the picture on our Ning network and we’ll post them - post them on Flickr or any other web service and let us know where they are
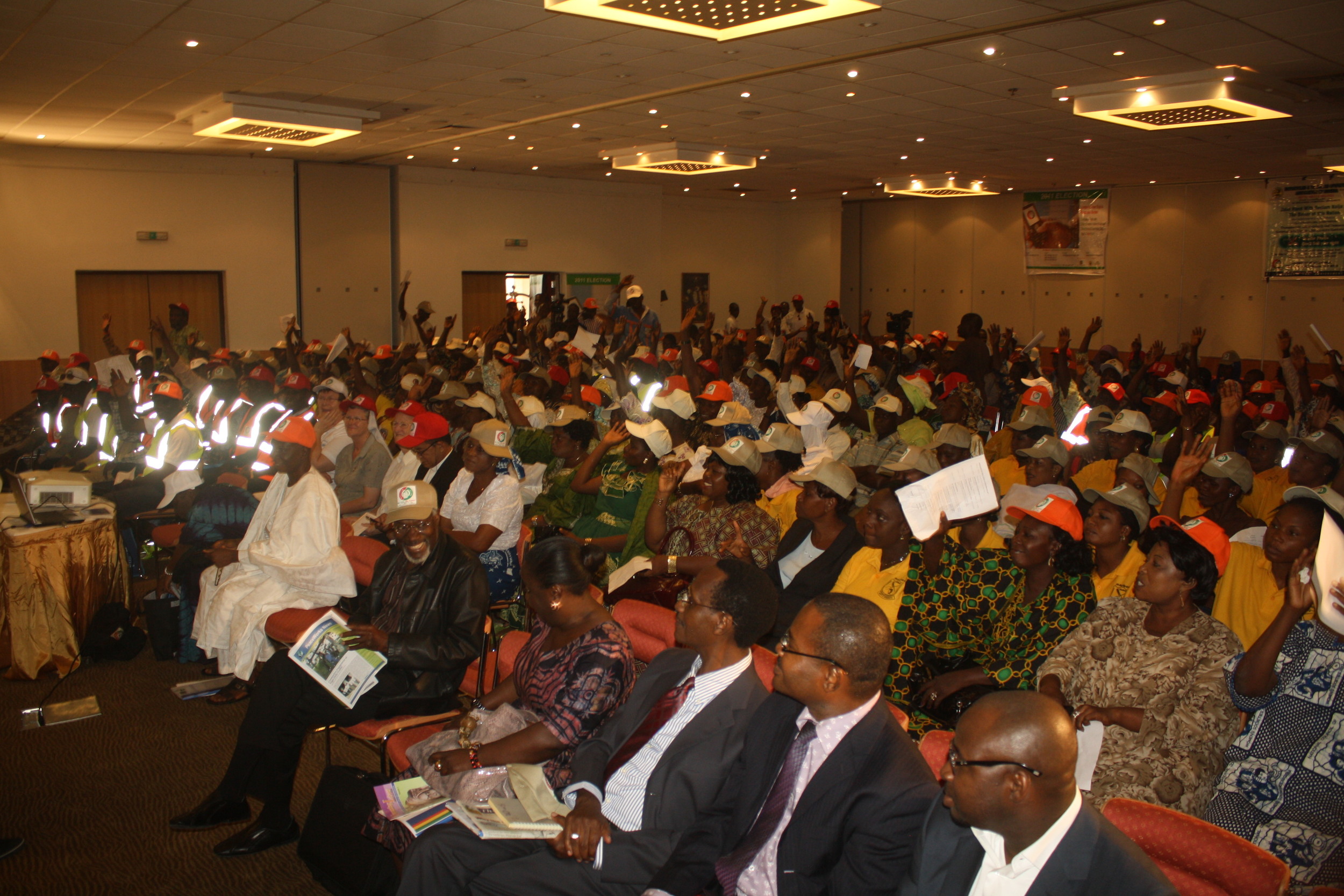
Coordinating FrontlineSMS Use in the Upcoming Kenyan Elections
Kenya’s upcoming elections will mark a pivotal moment in the country’s history. As in many countries, elections in Kenya become boiling points for interethnic conflict. The last presidential election, in December 2007, led to the worst violence the country has seen in recent history: over 1,300 Kenyans died and hundreds of thousands were displaced.
Although calm was restored within a few months, the country still faces several obstacles on its road to peace. The International Criminal Court will soon move to trials for four political elites accused of instigating the post-election violence. This increase in accountability may dampen future violence, but it also stokes tensions: two of the four intend to run for president, and their supporters smell politics behind the court’s process.
Another complicating factor is Kenya's new constitution, approved in a contentious but peaceful vote in August 2010. The new constitution decentralizes the government and puts more constraints on executive power. This lowers the stakes of winning the presidency, which should reduce the incentive for violence. However, decentralization also brings a potentially bewildering array of new offices to vote for, throwing a monkey wrench into political allegiances as well as election administration.
With the next general election now set to occur in March 2013, peacebuilders and democracy advocates in Kenya are looking for innovative ways to monitor election results and violence. Kenya’s high levels of mobile penetration and literacy create ideal conditions for a platform like FrontlineSMS.
One peacebuilding group, the African Great Lakes Initiative (AGLI), is building on its experience using FrontlineSMS to monitor Burundi’s 2010 elections. Working with its Democracy and Peace Groups in Burundi, AGLI provided cell phones and training to 160 citizen reporters in 9 communities. The citizen groups used the phones to report on election irregularities and violence, and used FrontlineSMS software to redistribute their reports to a larger group of community members.
AGLI plans to replicate and expand on this model in Kenya. The organization plans on recruiting and training one thousand citizen reporters in western Kenya. AGLI is also partnering with local government officials and other organizations to ensure effective responses to the information gathered. These types of relationships were critical to the system’s success in Burundi, as described by AGLI’s David Zarembka.
FrontlineSMS has been working to promote partnerships that make good use of the platform in Kenya’s elections. This has included hosting an online discussion where AGLI was joined in discussion by Konrad-Adenauer Foundation (KAS) and KAS’s partner Nyanza Partners for Peace Alliance, who are both part of the Partnerships for Peace project. The groups discussed effective ways to engage citizen reporters, as well as the benefits of open versus closed networks of reporters. Dave (AGLI) made the point that even a small-scale system can have a large impact. Hanna Carlsson of KAS and Joseph Owuondo of Nyanza Partners for Peace Alliance discussed the potential of pairing Crowdmap and FrontlineSMS together, and how this can create a powerful tool for advocacy, particularly at the international level.
To promote more collaboration, FrontlineSMS will host a meet-up in its Nairobi office (FF16 Bishop Magua Centre, Ngong Road, Kilimani) on 4 April, 1-2pm EAT. Representatives from various groups will be able to share ideas and coordinate action in the lead up to the elections. The ultimate aim of these efforts is to provide Kenyan and international actors with the information they need to ensure honest elections, combat political manipulation, and resolve conflicts before they turn violent. Given the negative impacts that further violence would have on Kenya and the region, this moment calls for creative ideas and dedicated implementation.
If you’re interested in this topic and/ or in attending the upcoming meet-up in Kenya please email info@frontlinesms.com to let us know. You can also join this forum discussion about the meet-up and the use of FrontlineSMS in the Kenyan elections.
This post was written by Dave Algoso, who is a development professional and writer based in Nairobi, Kenya. Dave normally blogs at Find What Works.
Nigerians Mobilize for Free and Fair Elections
This post is the latest in the FrontlineSMS Mobile Message series with National Geographic. To read a summary of the Mobile Message series click here. By Florence Scialom, Community Support Coordinator, FrontlineSMS
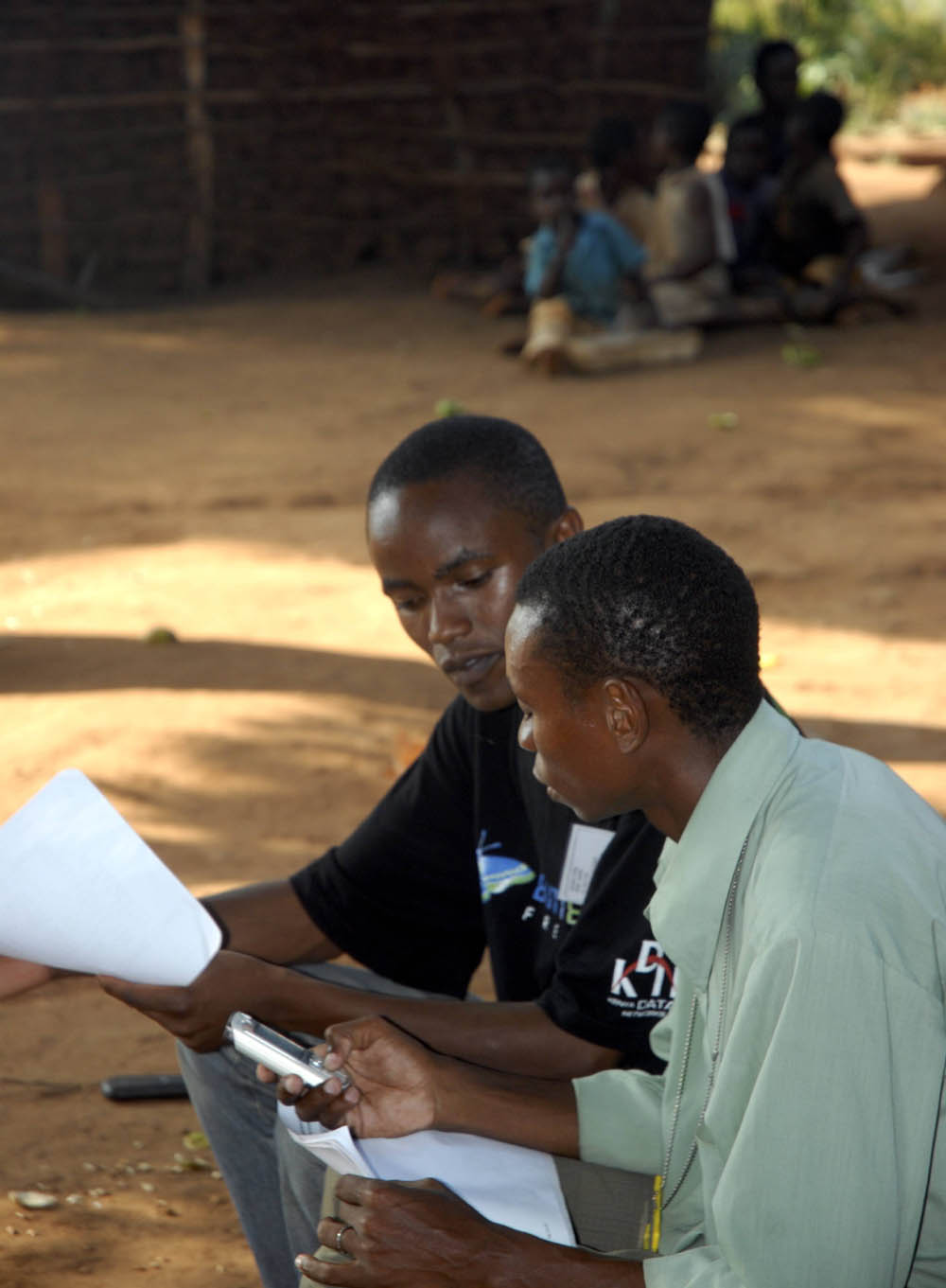
"A group of Nigerian grassroots organizations and agencies have joined together to form ReclaimNaija, in an effort to provide the Nigerian electorate a way to report on the elections as they happen. ReclaimNaija documents how citizens are experiencing the elections by using FrontlineSMS to receive and send text message reports, and Ushahidi to visually map the election reports received. It is very exciting to see FrontlineSMS being used in this way, especially because one of the first public use cases of the software was during the last Nigerian elections in 2007. As Community Support Coordinator at FrontlineSMS I have had the privilege of speaking to Ngozi Iwere from Community Life Project, one of the promoters of ReclaimNaija, as well as others who have been involved in helping with and using the platform. I have learned about how Community Life Project are encouraging citizens from grassroots communities all over the country to use mobile technology to amplify the voice of Nigerian citizens, making their opinions impossible to ignore.
Amidst the confusion of date changes surrounding the Nigerian elections one thing remains clear; the people of Nigeria are ready to vote. The 2011 Nigerian elections got off to an uncertain start; with the National Assembly elections due on April 2nd 2011 having to be pushed back as a result of many problems, leading to the rescheduling of the whole two week election process. Amongst the commotion of date changes it is more important than ever for the Nigerian public to feel they have a way to speak out about any election problems they experience, and know they are being heard.
Over the years, elections in Nigeria have been surrounded by controversy. “Since the return to civil rule in 1999, all the elections conducted in Nigeria have been marred by massive fraud and violence,” says Ngozi Iwere.
It is clear speaking with Nigerian citizens about ReclaimNaija that people are keen to actively challenge the problems previously accompanying their elections. “On election days, citizens have been frustrated by a number of things; missing names, seeing ballot boxes stuffed or even stolen and other electoral fraud and yet being unable to do anything about this. This time however, is the time to speak out” says Femi Taiwo, a member of INITS Limited, a Nigerian company that helped set up the technical side of ReclaimNaija’s monitoring system.
ReclaimNaija was established to “enhance the participation of grassroots people, organizations and local institutions in promoting electoral transparency, accountability and democratic governance in Nigeria” Ngozi Iwere tells me. ReclaimNaija achieved this participation in large part through voter education forums for community and grassroots leaders spread across the 36 States of the country and the Federal Capital Territory. As Ngozi explains “engaging the leaders of community-based social networks ensured that information got across to a large segment of society, as we trained leaders to pass on the message to their membership and constituencies.” Thus popular participation has been central to ReclaimNaija’s monitoring platform.During the January 2011 Voters Registration Exercise, ReclaimNaija received 15,000 reports from the public over two weeks. It is important “to have an election monitoring service that aids troubleshooting to expose and document fraud” says Ngozi Iwere. The election registration process proved this; on receiving messages about problems such as lack of registration cards ReclaimNaija was often able to communicate with the electoral body, thus helping improve the efficiency of the registration process.
Providing the option to make election reports via text message has improved the scope of ReclaimNaija’s work, helping them to target grassroots communities more effectively. “It is very important to have an election monitoring service that utilises tools that the average citizen is very familiar with” says Ngozi, explaining ReclaimNaija’s choice to provide the option for citizens to make reports via mobile phone.
Reflecting on the penetration levels that have made SMS such a powerful communications platform, Ngozi adds, “According to the Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC), Nigeria has 83 million active GSM lines.” Although the platform offered citizens other means of reporting, such as email, voice calls, Twitter, Facebook and direct reporting on the website, Ngozi explains they’ve found that “SMS was the most utilised medium both during the voter registration exercise and the aborted National Assembly Elections on Saturday 2nd April.”
The system clearly continues to be a powerful way for Nigerians to communicate throughout the recent date changes. The National Assembly elections, originally due on April 2nd 2011 were pushed back twice as a result of many problems, including lack of voting materials and staff absences at polling stations. The whole election process has now been re-scheduled. The National Assembly elections went ahead on 9th April, and they are due to be followed by the presidential poll on April 16th and the governorship election on April 26th. Confusion over the election dates left some Nigerians suspicious about the validity of the elections.
“There has been a lot of scepticism surrounding the 2011 elections, even more so with the recent postponement,” points out Nosarieme Garrick, a Nigerian who has made use of the ReclaimNaija reporting system and also works for VoteorQuench.org, a social media effort to get young Nigerians engaged in the elections. Nosarieme has observed that some people are assuming that the problems are orchestrated attempts to facilitate rigging.
In line with this, one message received through ReclaimNaija during the first attempt at the National Assembly election said “more than half of registered voters here [in my voting station] couldn’t find their names… Is this an attempt to reduce the number of voters in Lagos?”
However, Nosarieme suggests that having a service like ReclaimNaija has meant people are able to act on their concerns. “Reclaim Naija is allowing eyewitness accounts from average citizens to be collected on the actual happenings during elections, and people understand that their reports are not falling on deaf ears.” Furthermore, although Nigerians were unhappy at the postponement, there is also hope around improving the voting process. Nigerian Femi Taiwo explains “if shifting the date was what it was going to take to get it right this time around… then the postponement was the right thing to do.”
Citizens have been able to report a wide variety of issues – including electoral malpractices, corruption and incidences confusion and unrest. One would-be voter, for example, sent a message on the day National Assembly elections were due to start, stating, “here at Umudagu boot, no staff or material or any sign there will be election. Hundreds of voters are loitering without accreditation and it is 9.00am.”
These citizen reports have become a valuable source of information for the Independent National Electoral Commission (INEC), who are responsible for running the elections, thus representing the voice of the people to the authorities. ReclaimNaija collate reports and send directly on to the INEC in real time.
“If the INEC hadn’t seen these reports they would not have known about the level of problems being experienced by Nigerians; there would not have been this kind of proof” says Linda Kamau, an Ushahidi developer was in Nigeria to see the launch of ReclaimNaija system. There is clearly great power in ensuring the voices of the Nigerian people reach the authorities running the elections.
ReclaimNaija has been a great success so far, and in no small part due to the power of using SMS. As Ngozi Iwere explains, using mobile phones “puts the power of effective monitoring in the hands of the people.” Yet it is the Nigerian people themselves who are central to the process, and the technology is a facilitator for their participation. Ngozi makes clear “there is a deep yearning for change among the populace and citizens see this election as an opportunity to make that change happen.”
SMS used for peacekeeping at Burundi's Elections
The African Great Lakes Initiative (AGLI) strengthens, supports, and promotes peace activities at the grassroots level in the Great Lakes region of Africa (Burundi, Congo, Kenya, Rwanda, Tanzania, and Uganda). Here, in our twenty-ninth guest blog post, AGLI Coordinator, David Zarembka, discusses how FrontlineSMS proved a valuable tool for supporting and coordinating peace building efforts during recent election violence prevention in program in Burundi.
AGLI long ago learned that elections, rather than being a time of assessment, change and optimism, can, in the Great Lakes Region of Africa, often be a time of fear, unrest, and violence. Burundi is no exception. A traumatic civil war (1993-2006), instigated in part by the assassination of then president Melchoir Ndadaye, tore Burundian communities apart along “ethnic” lines and traumatized citizens on all sides. Tensions remain high, especially during election times. With this in mind as the 2010 Burundi elections approached, AGLI worked with the Healing and Rebuilding Our Communities (HROC) program in Burundi to develop the Burundi Election Violence Prevention Program.
during recent election violence prevention in program in Burundi.
AGLI long ago learned that elections, rather than being a time of assessment, change and optimism, can, in the Great Lakes Region of Africa, often be a time of fear, unrest, and violence. Burundi is no exception. A traumatic civil war (1993-2006), instigated in part by the assassination of then president Melchoir Ndadaye, tore Burundian communities apart along “ethnic” lines and traumatized citizens on all sides. Tensions remain high, especially during election times. With this in mind as the 2010 Burundi elections approached, AGLI worked with the Healing and Rebuilding Our Communities (HROC) program in Burundi to develop the Burundi Election Violence Prevention Program.
With a grant from the United States Institute of Peace, the project ran from May 2009 until October 2010 in nine communities across Burundi. The Program involved participatory community workshops to help heal trauma and encourage reconciliation. The 720 workshop participants were then organized into eighteen Democracy and Peace groups, two in each community to serve as the basis for observing the elections and preventing election violence in their local community.
While not part of the original proposal and based in part on the example set by the use of cell phones in Kenya in response to the 2008 post-election violence, staff decided that the program would benefit from taking advantage of recently developed technologies for networking via cell phones. The program staff decided to make use of FrontlineSMS, because it is an open source software program that allows people to send a single text message that is then rebroadcast to other members of a pre-defined set of users. In this case those users were citizen reporters who were part of the Democracy and Peace Groups as well as HROC staff.
Various technical delays and the lack of timely funding meant that the program did not get completely up and running as quickly as we would have liked. One of the challenges was that funding was not available to purchase the phones, and collecting 42 used phones which were donated from the UK and the US was time consuming. In early June 2010 additional funding was secured from Change Agents for Peace, International and used to buy a number of very cheap phones that provided a greater degree of standardization and allowed the inclusion of more participants.
 There were 160 citizen reporters who participated in the system. They were organized into nine groups, one for each community, as well as groups for HROC facilitators and staff. Training for the citizen reporters – to explain the basics of how to use the cell phones, how the phones would be used to promote the goals of the project, and how the phones would function with the FrontlineSMS system – were held in each of the nine communities.
There were 160 citizen reporters who participated in the system. They were organized into nine groups, one for each community, as well as groups for HROC facilitators and staff. Training for the citizen reporters – to explain the basics of how to use the cell phones, how the phones would be used to promote the goals of the project, and how the phones would function with the FrontlineSMS system – were held in each of the nine communities.
The skill level of the participants varied, ranging from people who were already familiar with using phones and sending text messages to people who had never used a phone, were barely literate, and had difficulty seeing the letters on the buttons and pressing the small buttons. Another minor challenge was that the FrontlineSMS system was occasionally overwhelmed with text messages, particularly on Election Day, which occasionally created delays.
Based on the record of the texts that were sent between June 25, 2010 and July 24, 2010, there were 735 text messages received from participants; about 12 messages per day. These were then re-distributed, and the system sent out 7,449 messages; about 124 per day.
The most frequent messages were those reassuring people that things were calm, followed by messages reporting incidents such as grenade attacks on polling stations, arrests, or other concerns. They were also used to share ideas with observers about possible irregularities for which they should be alert.
One particularly interesting series of text messages were explained by a participant during the evaluation interviews:
“On the eve of the presidential elections, everything was very tense, the bars were all closed, and the police were on high alert. Then I heard that three people were arrested that evening who we knew were not actually engaged in illegal activities. I texted [another member of the Democracy and Peace Group,], who agreed to follow up on the case with the police. From there, the two of us communicated by cell phones to coordinate our efforts to speak with various local officials and administrators. Eventually we heard from the Commune administrator that if one of us came the next morning we would see that they will be released. Later we heard from one of those arrested that one of the police officers was asking him, “Who are you that you have these administrators suddenly concerned about your status?” So it was really our coordination through the SMS network that helped these innocent people be released without harm.”
This indicates the type of coordination that was achieved through the FrontlineSMS network.
Participants suggested that there were in fact good reasons for having the option of text messaging. One advantage they mentioned was the possibility of privacy. For example, if one is witnessing an event first-hand it may not be possible to inform others by a traditional cell-phone call since people in the vicinity might overhear and might misunderstand the reasons why other people are being alerted, putting the observer at risk.
As with other communication tools, while the FrontlineSMS network enhanced the ways people were able to work together, ultimately the effectiveness of the network was a product of more traditional skills and relationships. The ease of communicating, and the ability to do so in a discrete way may have engaged citizens who would not otherwise have played an active role.
The group networks formed were functional and added to the overall program. Participants found the network useful for sharing information and keeping each other up-to-date. In this way the project set an important precedent for how similar networks might be used in the future.
For further information on how the Burundi Election Violence Prevention Program was organised, using FrontlineSMS as a tool, please see the AGLI Manual for Creating Democracy and Peace Groups to Prevent Election Violence.
Mobile meets citizen reporter in Mozambique
In this, the twentieth in our series of FrontlineSMS guest posts, Marcelo Mosse – Executive Director of the Centre for Public Integrity in Mozambique – talks about their use of the software in promoting citizen engagement in monitoring their national elections, and in their efforts to promote transparency in government "The Centre for Public Integrity of Mozambique (CIP) is a not-for-profit, non-partisan, independent organisation, endowed with legal status, and with administrative, financial and patrimonial autonomy. Our general objective is to promote integrity, transparency, ethics and good governance in the public sphere, and to promote human rights in Mozambique, and we use our website to launch campaigns, document events, and publish case studies and reports on Mozambique’s political process.
In 2008, local elections took place in Mozambique and the CIP decided to try using SMS to collect events reported by citizens. We implemented FrontlineSMS and launched a press campaign aimed at making the public aware of the opportunity to report and comment on events on the electoral campaign, and events at the voting posts.
Telephone lines were made available and FrontlineSMS was installed and used by CIP staff in charge of coordinating the publishing of text messages on our website. Response from the citizens was considered satisfactory – with mobile phones in use over most of the country and accessible to almost all economic level layers, citizens showed they were eager to contribute.

Later in 2009, during the general elections in Mozambique, we increased the number of available lines for the public and launched a more comprehensive campaign (newspapers, television, and radio). The outcome was considered very satisfactory with SMSs being received right from the beginning of the electoral campaigns. FrontlineSMS was also used to get instant reports from the CIP’s correspondents placed at the 43 municipalities all over the country.
Thanks to FrontlineSMS we were able to compile reports on party and candidate practices during the electoral campaigning, citizen’s reactions and opinions on the electoral process and anomalies at the voting posts.
User experience from those using the software was positive. It was easy to understand and operate, to add phones, and manage and classify messages received. The CIP intends to continue using FrontlineSMS on other campaigns where we believe citizen contribution can be valuable".
Marcelo Mosse Executive Director Centre for Public Integrity Mozambique www.cip.org.mz
BBC: Texts monitor Nigerian elections
"We want to set a precedent," said Emauwa Nelson of the Human Emancipation Lead Project, a Nigerian NGO that helped set up the project."We want people to know that if they are trying to rig the election, there could be someone behind them and that person may send a text message saying what happened."