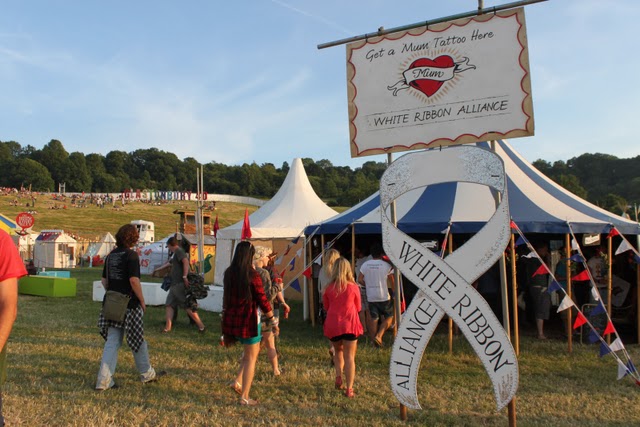
Our twenty-sixth guest post comes from the lovely James at the White Ribbon Alliance, who piloted FrontlineSMS in campaigning in a particularly innovative and fun bit of awareness-raising - offering free transfer tattoos at Glastonbury Festival... The White Ribbon Alliance for Safe Motherhood is a coalition of individuals and organisations that campaign to make pregnancy and childbirth safe for all women and newborns. With members in 148 countries, I had thought for a while that FrontlineSMS could be a very useful tool for many of our members, so was keen to "road-test" the software when the opportunity presented itself.
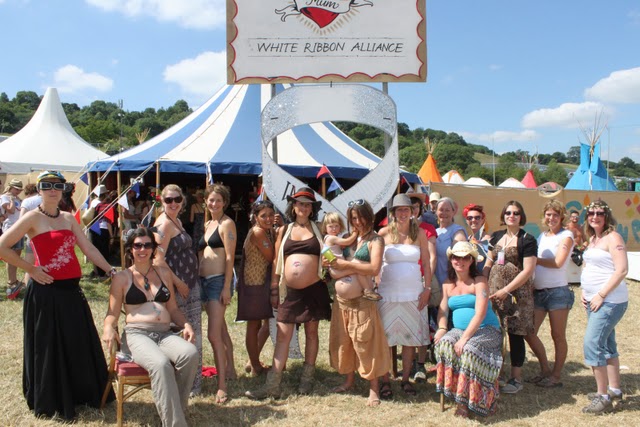
Glastonbury Festival seemed like a great opportunity to do so. For the second year running, we were running a campaign to raise awareness of Maternal Health - by offering people the ultimate way to show how much they love their mum - by coming to our "tattoo parlour" and having a classic "mum" heart tattoo.
In the first year, we were taken aback by the amazing response and the vast number of people that got a tattoo and signed up to be part of our movement. However, this left us with thousands of people's handwritten contact details to type up onto the computer for our mailing lists, which made it really difficult for us to get back to them quickly and simply.
So, this year, I downloaded FrontlineSMS, bought an old electric pink Sony Ericsson phone and USB cable from the Queensway Computer Market (for any London dwellers, this is a veritable Aladdin's cave of old phones, computers and parts), and a SIM card, so that people could text us their email addresses instead.
I had a couple of hiccups setting up FrontlineSMS with the phone - firstly, drivers weren't available for, or didn't work with, Windows 7 - which meant that computer that I'd been putting off upgrading from Windows XP was suddenly my least favourite machine in the office no more - and then the first set of drivers that I downloaded for the phone didn't allow FrontlineSMS to see the handset.
However, a quick search for the phone's model number on FrontlineSMS's forums turned up a link for alternative drivers, which linked the phone up and meant it could send and receive texts perfectly.
Not wanting to risk taking a laptop to the muddy fields of Somerset, I anxiously left the computer in the office running FrontlineSMS with my fingers crossed that it wouldn't crash and that no-one turned it off whilst I was at the festival.
Happily though, when I returned, everything was still running - and a couple of minutes later, I had exported all the email addresses into a nice .csv file ready to be imported into our mailing list server! Unfortunately, we still had thousands of handwritten signups to transcribe. Whilst I don't think we'll ever eliminate this, FrontlineSMS seems like a really effective way to reduce the use of paper, offer easier ways for people to ask for more information about our campaigns, and for us to get back in contact with them.
Perhaps more importantly, it proved itself a reliable tool that I think has the potential to be really useful to our members around the world - and we look forward to introducing them to it and hearing their thoughts and ideas of how they might use it for their own work in support of Maternal Health.
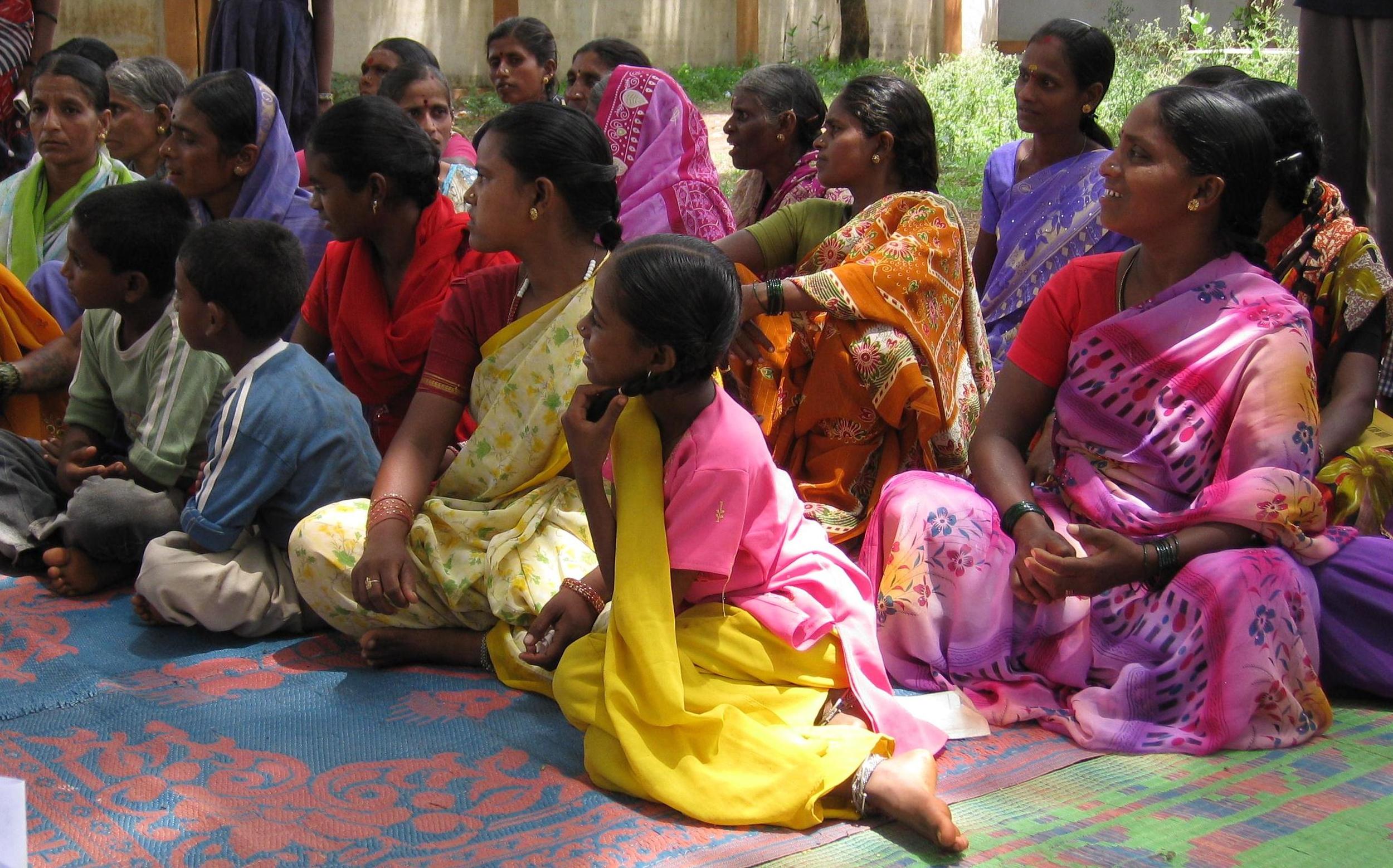







 Due to this serious situation, and the necessity to improve the collection of information, TSF, in collaboration with PATH (an international non-profit organisation that aims at enabling communities worldwide to break longstanding cycle of poor health) is reinforcing SILAIS’ capacities in Information and Communications Technologies.
Due to this serious situation, and the necessity to improve the collection of information, TSF, in collaboration with PATH (an international non-profit organisation that aims at enabling communities worldwide to break longstanding cycle of poor health) is reinforcing SILAIS’ capacities in Information and Communications Technologies.





